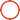
The manufacturing process of an **LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) panel** involves several complex steps, from substrate preparation to final assembly. Below is a detailed breakdown of the key stages:
1.taking in-----2.cleanning-----3.P.R coating----4.Pre.bake----5.exposure----6.develop-----7.post bake----8.Etching-----9.strip-----10.cleanning-----11.PI coating ------12.Pre. bake----13.oven----14.Rubbing----15.short print---16.spacer spray-----17.seal print----18.assembly---19 hot press--20.oven
1. Substrate Preparation (Glass Substrate)**
Material: Thin, high-purity glass (e.g., Corning’s Eagle XG).
- **Process::
- Glass is cut into large sheets (e.g., Gen 10.5: 3370×2940 mm).
- Cleaned to remove impurities (ultrasonic cleaning, chemical treatment).
2. Thin-Film Transistor (TFT) Array Fabrication**
- **Purpose:** Creates the active matrix that controls each pixel.
- **Steps:**
1. **Deposition:** A thin layer of semiconductor (amorphous silicon or IGZO) is deposited via **PECVD** (Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition).
2. **Patterning:** Photolithography defines the TFT circuits:
- Coating with photoresist.
- UV exposure through a mask.
- Etching (wet/dry) to remove unwanted material.
3. **Metallization:** Sputtering deposits metal (Al, Cu, or Mo) for electrodes and interconnects.
4. **Repetition:** The process is repeated 4–5 times to build the full TFT layer.
---
3. Color Filter (CF) Substrate Fabrication**
- **Purpose:** Adds red, green, and blue (RGB) color filters to the opposing glass substrate.
- **Steps:**
1. **Black Matrix (BM):** A light-blocking layer (chrome or resin) is patterned to separate pixels.
2. **Color Filter Printing:** RGB pigments are applied via **photolithography** or inkjet printing.
3. **Overcoat Layer:** A protective acrylic resin is applied.
4. **ITO Layer:** A transparent conductive layer (Indium Tin Oxide) is sputtered for the common electrode.
---
4. Liquid Crystal (LC) Cell Assembly**
- **Alignment Layer:** Polyimide is coated on both TFT and CF substrates, then rubbed to align LC molecules.
- **Spacers:** Tiny plastic beads/spacers are sprayed to maintain uniform cell gap (~3–5 µm).
- **Sealing:** The two substrates are bonded with a UV-cured adhesive, leaving a fill port.
- **LC Injection:** Vacuum fills the gap with liquid crystals (nematic, IPS, VA, etc.).
- **Sealing the Port:** The fill hole is sealed.
---
*5. Polarizer Attachment**
- **Polarizing Films:** Applied to the outer sides of the panel (typically at 90° angles for brightness control).
- **Compensation Films:** Added for wider viewing angles (e.g., WV films for IPS panels).
---
*6. Backlight Integration (for Transmissive LCDs)**
- **Components:**
- **Light Guide Plate (LGP):** Spreads light evenly (edge-lit) or direct-lit LEDs.
- **Diffuser/Prism Sheets:** Enhance brightness uniformity.
- **LED Arrays:** White LEDs provide the light source.
- **Assembly:** The backlight unit (BLU) is attached behind the LCD panel.
7. Driver IC Bonding**
- **Chip-on-Glass (COG):** Driver ICs are bonded to the glass edges using anisotropic conductive film (ACF).
- **Flexible PCBs:** Connect the panel to external control circuits.
8. Final Testing & Module Assembly**
- **Electrical Testing:** Checks for dead pixels, TFT defects, and color uniformity.
- **Aging Test:** Panels are stressed to ensure reliability.
- **Module Assembly:** Integrated with touch sensors (if touchscreen), bezel, and connectors.
**Key Variations by LCD Type**
- **TN (Twisted Nematic):** Fast response, lower cost.
- **IPS (In-Plane Switching):** Better color accuracy, wider viewing angles.
- **VA (Vertical Alignment):** High contrast, deeper blacks.
---
Challenges & Advancements
- **Yield Issues:** Dust particles can ruin TFT arrays (cleanrooms required).
- **New Tech:** Mini-LED backlights, quantum dot enhancements (QLED), and OLED competition.